Symptoms of an occluded carotid artery can often be subtle but may lead to serious health issues if left unnoticed. You might experience transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), which can manifest as sudden weakness or numbness, especially on one side of your body. Additionally, you may notice confusion, difficulty speaking, or vision changes. Recognizing these signs early can significantly impact your health journey and help you seek appropriate medical care.
What is an Occluded Carotid Artery?
Understanding Carotid Arteries
Carotid arteries run along each side of your neck and are responsible for delivering oxygen-rich blood from your heart to your brain. These arteries bifurcate into the internal and external carotid arteries, with the internal carotid artery primarily supplying blood to your brain and the external supplying blood to your face and neck. When engaging in activities that require mental focus or physical exertion, the demand for adequate blood flow through these arteries increases, highlighting their importance in maintaining optimal brain health.
Any significant disturbance in blood flow through your carotid arteries can have serious implications. An occlusion, or blockage, can restrict blood supply, leading to symptoms like dizziness, vision changes, or even more severe complications such as stroke. Your understanding of these vessels helps you appreciate their vital role in overall health and the potential consequences of their obstruction.
Why They Can Get Occluded
Occlusion of the carotid artery typically results from atherosclerosis, where fatty deposits known as plaques build up on the artery walls, narrowing the passage for blood. These plaques can form due to factors like high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes. Such conditions not only promote the accumulation of plaque but also weaken arterial walls, making them susceptible to rupture, which can precipitate acute blockages.
Your lifestyle choices, including diet and physical activity levels, significantly impact the health of your carotid arteries. For instance, consuming a diet high in saturated fats and sugars can elevate cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of plaque formation. Additionally, chronic stress and insufficient physical exercise contribute to vascular health decline, potentially leading to more severe complications over time.
Genetic predisposition also plays a role in the likelihood of carotid occlusion. If you have a family history of cardiovascular disease, your risk factors might include inherited issues like high cholesterol or hypertension. It’s vital to stay proactive in monitoring your heart health through regular check-ups and lifestyle modifications.
Common Symptoms to Watch For
Stroke Symptoms
If you have an occluded carotid artery, one of the most alarming symptoms to be aware of is that of a stroke. You might experience sudden weakness or numbness on one side of your body, particularly in your arm, leg, or face. This can occur without warning and may be accompanied by confusion or difficulty speaking. If you notice these symptoms, it’s vital to act immediately, as prompt medical care can significantly impact outcomes.
Visual disturbances, such as sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes, can also indicate a stroke. You may find it challenging to maintain your balance or coordination, leading to unexpected falls. These signs are often transient, lasting only a few minutes, which can create a false sense of security. However, any episode like this should be taken seriously.
Other Warning Signs
Aside from stroke-related symptoms, you might experience a range of additional warning signs of an occluded carotid artery. These could include persistent headaches, particularly if they manifest suddenly and with intensity. You could also notice changes in your speech patterns, such as difficulty finding the right words or slurred speech.
Moreover, if you encounter unexpected fatigue or a general feeling of unwellness, these could be subtle indicators of impending issues. Always consult a healthcare professional when such symptoms arise, even if they seem minor, as early detection and intervention can prevent further complications.
Risk Factors for Occlusion
Several factors can contribute to the formation of blockages in your carotid arteries. Understanding these risk factors can help you take proactive steps towards maintaining your vascular health. Some of the most significant risk factors include:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Family history of cardiovascular disease
This comprehensive understanding allows you to manage your health effectively and potentially reduce your chances of developing serious complications related to an occluded carotid artery.
Lifestyle Choices
Your daily habits play a significant role in your overall cardiovascular health. Choices such as consuming a well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can significantly lower the risk of arterial occlusion. On the other hand, a diet high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can lead to the buildup of plaque in your arteries. Furthermore, regular physical activity not only helps in managing weight but also aids in maintaining healthy blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Moreover, avoiding smoking can’t be overstated; it damages blood vessels and accelerates the buildup of fatty deposits, increasing your risk of occlusion. Limit alcohol intake and reduce stress through mindfulness practices or regular exercise. Building these healthy habits is vital for protecting your carotid arteries over time. This consistent attention to your lifestyle choices can significantly reduce your vulnerability to vascular diseases.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can increase the likelihood of experiencing an occluded carotid artery. For example, hypertension and hyperlipidemia lead to deterioration in blood vessel health. Conditions like diabetes greatly amplify your risk profile due to their effects on arterial walls, making them more susceptible to plaque buildup.
Other conditions, such as chronic kidney disease and obstructive sleep apnea, can also contribute to the likelihood of carotid artery occlusion. Individuals with these conditions often experience additional cardiovascular strain, which can lead to further progression of disease within their arterial systems. This interplay of medical issues underlines the importance of regular check-ups and effective management of existing health conditions to mitigate risks associated with carotid artery occlusion.
Diagnosis of Occluded Carotid Artery
Imaging Tests
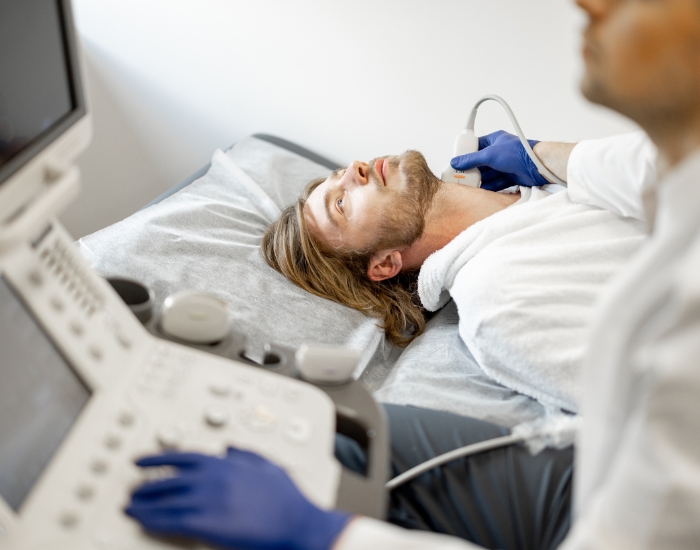
Imaging tests play a vital role in the diagnosis of an occluded carotid artery. Doppler ultrasound is often the first-line test, providing real-time imaging and blood flow measurement. This non-invasive method allows your physician to detect any blockages or narrowing in the carotid arteries by evaluating the velocity of blood flow. In cases where further detail is needed, a CT angiography or MRI angiography may be recommended, which offers a detailed view of the blood vessels and can accurately assess the extent of occlusion.
Additionally, a traditional angiogram may be performed as a more invasive option, where a catheter is inserted through your groin or arm to directly visualize the arteries. This test not only confirms the presence of an occlusion but can also be used to guide treatment options, such as angioplasty or stenting if necessary.
Physical Examination
Your physician will also conduct a thorough physical examination to assess the risk factors and symptoms associated with an occluded carotid artery. During the examination, they will listen for bruits, which are abnormal sounds that may indicate turbulent blood flow due to a narrowing or blockage. This can be detected using a stethoscope placed over your carotid arteries.
In addition to checking for bruits, a thorough evaluation of your blood pressure, pulse, and overall cardiovascular health will be conducted. Your doctor may also review your medical history and any existing risk factors, such as high cholesterol, diabetes, or smoking, which can contribute to arterial occlusion.
Physical examination results can provide valuable insight beyond just the symptoms you report. For instance, noticing certain signs related to circulation or checking for other vital health markers can help your physician make more informed decisions about the next steps in your diagnosis and treatment plan.
Treatment Options
Medical Management
In managing an occluded carotid artery, medical management often serves as the first line of defense. Your doctor may prescribe anticoagulants or antiplatelet medications to reduce the risk of blood clots. For instance, Aspirin or Clopidogrel can significantly lower your chances of stroke by preventing additional clot formation. Additionally, cholesterol-lowering drugs like statins might be recommended to stabilize plaque within the arteries, decreasing the chances of further obstruction.
Furthermore, lifestyle modifications play a vital role in your treatment plan. Emphasizing a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing weight can positively affect your overall cardiovascular health. You’ll also want to keep an eye on underlying conditions such as hypertension or diabetes, as effectively controlling these can significantly enhance your health outcomes.
Surgical Interventions
When medical management proves insufficient, your doctor may explore surgical interventions. One common procedure is a carotid endarterectomy, where the surgeon removes plaque from the artery to restore blood flow. This option is typically recommended if the blockage is severe and symptoms like transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) have occurred. Another procedure is carotid artery stenting, which involves placing a stent to keep the artery open. Your doctor will assess which option best suits your specific condition.
The choice between these surgical options often depends on factors such as the severity of the occlusion, your overall health, and previously mentioned symptoms. For example, studies indicate that carotid endarterectomy has a lower risk of stroke during the procedure compared to stenting but may require a longer recovery time. Understanding these differences will help you make informed decisions alongside your healthcare provider.
Prevention Strategies
Healthy Lifestyle Tips
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce your risk of experiencing an occluded carotid artery. Emphasize a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Incorporate heart-healthy fats, such as those found in avocados and nuts, while limiting saturated and trans fats. Regular physical activity, aiming for at least 150 minutes per week, can enhance your blood circulation and support overall cardiovascular health. Additionally, managing your weight and maintaining a healthy blood pressure are pivotal in reducing the likelihood of arterial blockages.
- Balanced diet
- Regular exercise
- Weight management
- Smoke cessation
- Limit alcohol consumption
This holistic approach not only supports your cardiovascular health but also contributes to overall well-being.
Regular Check-ups
Scheduling regular check-ups with your healthcare provider is important in monitoring your cardiovascular health. These visits allow your doctor to assess your risk factors, perform necessary screenings, and provide tailored recommendations for maintaining arterial health. Early identification of high cholesterol, hypertension, or diabetes can help prevent worsening conditions that could lead to an occluded carotid artery.
In addition to routine physical exams, your doctor may recommend specific tests such as blood tests and imaging to evaluate your vascular health. Interventions taken at regular intervals can help you stay ahead of potential risks and ensure that you are taking effective strides towards preventing complications associated with occluded arteries.
Final Words
Considering all points, being aware of the symptoms related to an occluded carotid artery can significantly enhance your ability to seek timely medical attention. You may experience warning signs such as sudden numbness or weakness, especially in one side of your body, difficulty speaking, or vision changes. It’s important to listen to your body and take action if you notice any of these symptoms, as they can be indicative of more serious conditions, including a stroke.
Your health is paramount, and understanding the potential signs of an occluded carotid artery allows you to be proactive about your wellbeing. Staying informed and vigilant can empower you to engage your healthcare provider early, leading to better outcomes and a healthier life. Ensuring regular check-ups and discussing any concerns with your doctor can serve as a proactive measure towards protecting your cardiovascular health.
FAQ
Q: What are the common symptoms of an occluded carotid artery?
A: Common symptoms include sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body, confusion, trouble speaking or understanding speech, difficulty seeing in one or both eyes, and sudden severe headache.
Q: Can an occluded carotid artery cause dizziness?
A: Yes, patients may experience dizziness or lightheadedness due to reduced blood flow to the brain as a result of an occluded carotid artery.
Q: Is there a specific sign indicating a severe blockage in the carotid artery?
A: A transient ischemic attack (TIA), often called a mini-stroke, can indicate severe blockage and may present with temporary symptoms such as weakness, difficulty speaking, or loss of vision that resolve quickly.
Q: How might an occluded carotid artery affect daily activities?
A: Patients may find it difficult to perform daily activities due to weakness, balance issues, or cognitive impairment from insufficient blood flow, impacting their ability to walk, talk, or think clearly.
Q: When should someone seek medical attention for suspected occluded carotid artery symptoms?
A: Immediate medical attention is warranted if someone experiences sudden symptoms such as numbness, confusion, or vision changes, as these could indicate a stroke or severe blockage requiring urgent care.