Varicose Veins: Causes, Symptoms and Treatments
Varicose veins are a common vascular condition that affects millions of people worldwide. These abnormal, enlarged veins typically appear on the legs and feet, causing discomfort, pain, and cosmetic concerns for many individuals. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options available for varicose veins.
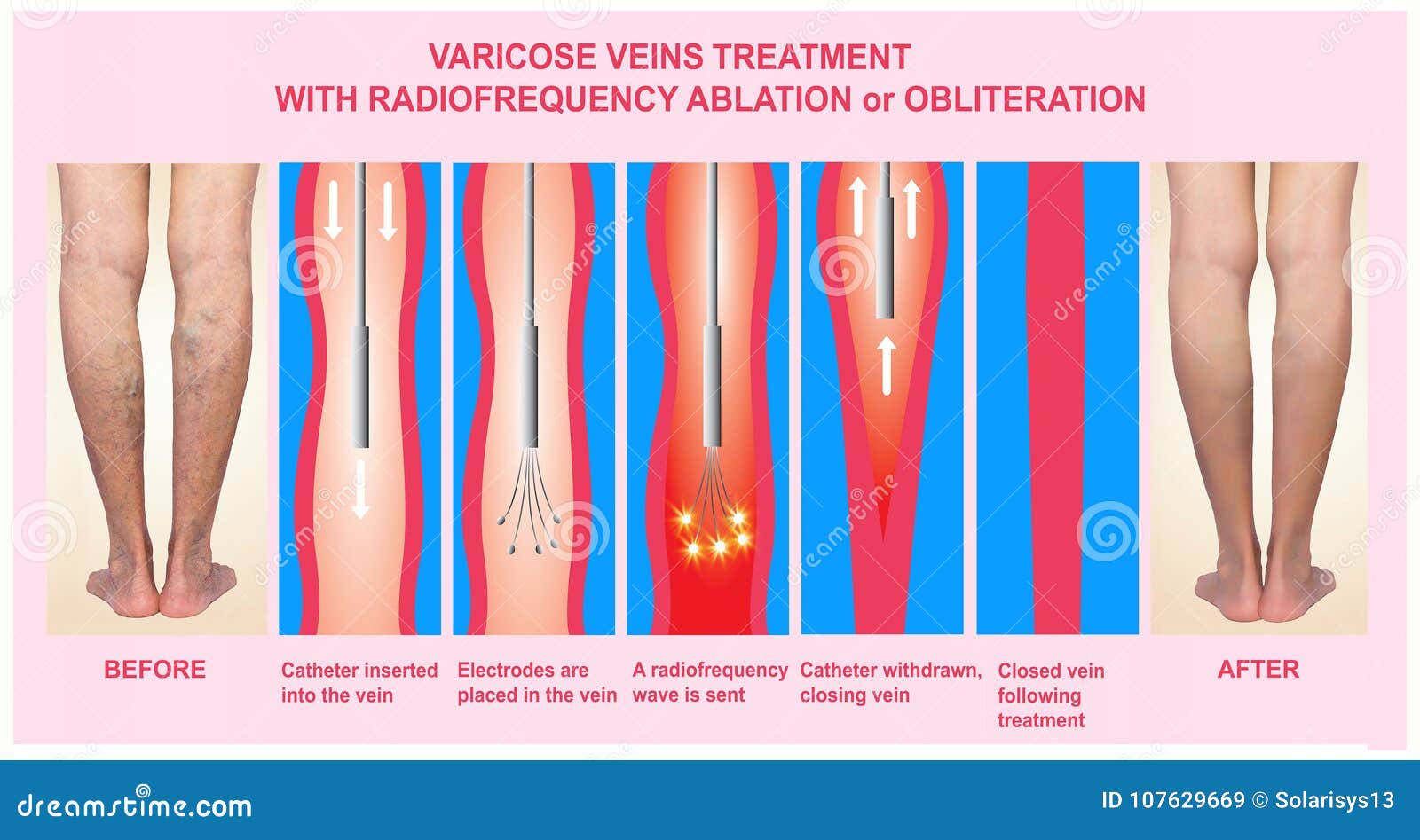
Table of Contents
Varicose veins are a widespread vascular ailment that impacts millions of individuals globally. These abnormal, enlarged veins typically appear on the legs and feet, causing discomfort, pain, and cosmetic concerns for many individuals. In this extensive manual, we will explore the origins, indicators, and numerous treatments accessible for varicose veins.
What are Varicose Veins?
Varicose veins are twisted, swollen veins that bulge beneath the skin's surface. They often take on a bluish or purplish hue and can be easily visible, especially on the legs and feet. These veins develop when the valves inside the veins, which are responsible for directing blood flow back to the heart, become weakened or damaged. As a result, blood begins to pool in the veins, causing them to stretch and enlarge.
Several factors can contribute to the development of varicose veins, including:
- Genetics: Having a family history of varicose veins increases your risk of developing them.
- Age: As we age, our veins lose elasticity, and the valves may not function as effectively.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop varicose veins due to hormonal changes during pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause.
- Obesity: Excess body weight puts additional pressure on the veins, making it harder for them to efficiently pump blood back to the heart.
- Prolonged standing or sitting: Jobs or lifestyles that involve long periods of standing or sitting can lead to poor circulation and increased pressure on the veins.
Symptoms of Varicose Veins
While some people with varicose veins may not experience any symptoms, others may encounter various signs and discomforts, including:
- Aching, heaviness, or cramping in the legs
- Swelling in the feet and ankles
- Itching or burning sensation around the affected veins
- Skin discoloration or texture changes near the varicose veins
- Pain that worsens after prolonged standing or sitting
- Restless leg syndrome
If left untreated, varicose veins can lead to more serious complications such as skin ulcers, blood clots, or bleeding. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any of these symptoms or notice significant changes in your veins' appearance.
Diagnosing Varicose Veins
To diagnose varicose veins, your doctor will typically perform a physical examination and assess your medical history. They may ask about your symptoms, lifestyle factors, and family history of vascular conditions. In some cases, additional tests may be necessary to evaluate the extent of the problem and rule out other underlying health issues. These tests may include:
- Duplex Ultrasound: This non-invasive test uses sound waves to create images of the blood flow in your veins, helping to identify any abnormalities or blockages.
Treatment Options for Varicose Veins
Treatment for varicose veins depends on the severity of the condition, the presence of symptoms, and the individual's overall health. Some common treatment options include:
-
Lifestyle Changes: Making simple lifestyle adjustments can help manage and prevent varicose veins. These include maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, avoiding prolonged standing or sitting, elevating your legs when resting, and wearing compression stockings.
-
Compression Stockings: These specially designed stockings apply gentle pressure to the legs, helping to improve blood flow and reduce swelling and discomfort associated with varicose veins.
-
Sclerotherapy: A minimally invasive procedure that involves injecting a chemical solution into targeted veins, causing them to collapse and gradually disappear. It is commonly used for treating smaller varicose veins and spider veins.
-
VenaSeal: VenaSeal is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a medical adhesive to seal off the affected veins. The adhesive is delivered through a small catheter inserted into the vein, causing it to close and redirect blood flow to healthy veins.
-
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): RFA, also known as the ClosureFast procedure, uses radiofrequency energy to heat and seal the affected vein. A small catheter is inserted into the vein to deliver the energy, causing the vein to collapse and close. RFA has largely replaced traditional vein stripping surgery as it can be performed under local anesthesia with faster recovery and fewer complications.
-
Endovenous Laser Ablation: This procedure involves inserting a thin laser fiber into the varicose vein and using heat energy to seal it shut. The treated vein will eventually be absorbed by the body, and blood flow will be redirected to healthier veins.
-
Ambulatory Phlebectomy: In this surgical procedure, small incisions are made in the skin, and the varicose veins are removed through these incisions. This method is typically reserved for larger, more prominent varicose veins.
It is essential to discuss the various treatment options with your healthcare provider to determine the most suitable approach for your specific case. They will consider factors such as the size and location of your varicose veins, your symptoms, and your overall health when recommending a treatment plan.
Preventing Varicose Veins
While some risk factors for varicose veins, such as age and genetics, cannot be changed, there are several steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing them or prevent existing ones from worsening:
-
Maintain a healthy weight: Excess body weight puts added pressure on your veins, so maintaining a healthy BMI can help reduce your risk.
-
Exercise regularly: Engaging in physical activities that promote circulation, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, can help keep your veins healthy and prevent blood from pooling.
-
Avoid prolonged standing or sitting: If your job or lifestyle involves long periods of standing or sitting, take frequent breaks to move around and stretch your legs.
-
Elevate your legs: When resting or sleeping, elevate your legs above your heart level to improve blood flow and reduce pressure on your veins.
-
Wear compression stockings: If you are at high risk for varicose veins or have a family history of the condition, wearing compression stockings can help promote better blood flow and prevent the formation of new varicose veins.
Conclusion
Varicose veins are a prevalent vascular condition that can cause discomfort, pain, and cosmetic concerns for many individuals. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available, you can take proactive steps to manage and prevent this condition. If you believe you may have varicose veins or are noticing any associated symptoms, it is imperative to seek advice from a medical professional for a precise evaluation and customized treatment strategy. With the right approach and lifestyle modifications, you can effectively manage varicose veins and maintain healthy, comfortable legs.
- Varicose Veins
- Vein Disease
- Symptoms
Tommy Nguyen
Content Writer